使用场景包括最常见的工具场景,比如自动插入一些逻辑代码,或批量修改相同的代码逻辑等等。
本文介绍了一种利用 AST 修改代码的方案,阅读本文需要了解一些编译原理基础,如果你还不了解,推荐看看这个,快速了解。
什么是 AST
引用维基百科:
在计算机科学中,抽象语法树(Abstract Syntax Tree,AST),或简称语法树(Syntax tree),是源代码语法结构的一种抽象表示。它以树状的形式表现编程语言的语法结构,树上的每个节点都表示源代码中的一种结构。之所以说语法是“抽象”的,是因为这里的语法并不会表示出真实语法中出现的每个细节。
AST 能干什么
- IDE 的错误提示、代码格式化、代码高亮、代码自动补全等
- eslint 等对代码错误或风格的检查、修复等
- webpack、rollup、babel 进行代码打包等
- CoffeeScript、TypeScript、JSX 等转化为原生 Javascript
- …
如何操作
假如有以下代码,我们想引入 store,并注入构造参数中:
import Vue from "vue";
import App from "./App";
import router from "./router";
new Vue({
el: "#app",
render: h => h(App),
router,
});
得到 AST
首先我们得有一个对应语言的 parser ,下面以 js 为例,我直接选开源的 @babel/parser 了,照着文档敲:
const parser = require("@babel/parser");
const entryContent = fs.readFileSync(filepath, "utf-8");
const AST = parser.parse(entryContent, {
sourceType: "module",
});
在调试面板中可以看到,四个顶层节点与代码一一对应:

修改 AST
第一步,我们想在 router 后面追加 store 的引用。遍历 AST 可以用 @babel/traverse ,也可以自己手动写循环,出于性能考虑,官方也推荐我们自己手动循环:
// 找到相对节点
let routerImportDeclarationIndex = 0;
let newVueExpression;
AST.program.body.forEach((node, i) => {
if (node.type === "ImportDeclaration") {
if (node.specifiers && node.specifiers[0].local.name === "router") {
routerImportDeclarationIndex = i;
}
} else if (node.type === "ExpressionStatement") {
if (node.expression.type === "NewExpression") {
newVueExpression = node;
}
}
});
我们用 @babel/type 来生成节点
const t = require("@babel/types");
// 插入 `import store from './store'`
AST.program.body.splice(
routerImportDeclarationIndex,
0,
t.importDeclaration([t.importDefaultSpecifier(t.identifier("store"))], t.stringLiteral("./store"))
// 小技巧:等同于 t.identifier(`import store from './store'`)
);
// 注入构造参数
newVueExpression.expression.arguments[0].properties.push(
t.objectProperty(t.identifier("store"), t.identifier("store"), false, true)
);
AST 转成代码
接下来就是将这个新 AST 转换成代码了:
const babel = require("@babel/core");
let { code } = babel.transformFromAstSync(AST, entryContent, {
generatorOpts: {
jsescOption: {
// escapeEverything: false,
quotes: "single",
},
},
babelrc: false,
configFile: false,
presets: [],
});
// 中文反转义,选项里没找到相关配置,只能先手动处理一下了
code = code.replace(/\\u([\d\w]{4})/gi, (m, g) => String.fromCharCode(parseInt(g, 16)));
fs.writeFileSync(filepath, code);
整个过程到此就结束了。
vue 文件的 AST 读写
任何语言都有相应的编译器,Vue 也是。说到这里,你是不是想到了 vue-template-compiler? 先来试一下看看效果吧:
const compiler = require("vue-template-compiler");
const sfcDescriptor = compiler.parseComponent(fs.readFileSync(filePath, "utf-8"));
sfcDescriptor 长这样:
interface SFCDescriptor {
template: SFCBlock | undefined;
script: SFCBlock | undefined;
styles: SFCBlock[];
customBlocks: SFCBlock[];
}
interface SFCBlock {
type: string;
content: string;
attrs: Record<string, string>;
start?: number;
end?: number;
lang?: string;
src?: string;
scoped?: boolean;
module?: string | boolean;
}
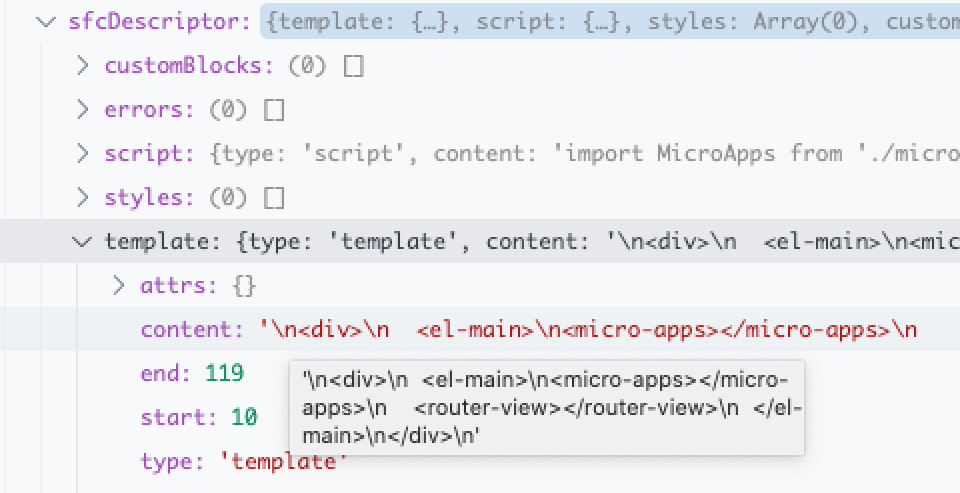
可以看到,sfcDescriptor(single file component descriptor) 的地位就相当于 vue ast (vast) 了,只不过结构更简单了。
因为 vue 的不同区块又是不同的语言,区块内容可以根据区块的语言交给下一个 parser 处理,例如:
sfcDescriptor.script.lang === void 0 || sfcDescriptor.script.lang === 'js'时,我们把 sfcDescriptor.script.content 交给 babel 处理。
默认 js,如果这里写了
lang: 'js', 那么生成代码时会多出一个lang属性<script lang="js"></script>
我们只需要把 sfcDescriptor (vast) 再转成代码即可。(官方没找到对应的包,我随便搜了一个,vue-sfc-descriptor-stringify,目前没遇到啥问题。)
踩过的坑
最开始 vast.template.content 用的 vue-template-compiler 处理的,但是缺点太多:
- 官方没有提供
transform方法 - 处理太复杂,要区分各种指令、修饰符…
- 转换出来的 AST 细节丢失严重
- 注释节点丢失
- 无法分辨缩写,比如:
v-on还是@
前两点还能忍,第三点对于这个场景来说,完全是不能接受的。当然,vue-template-compiler 是被设计用来生成 render function 的,也不怪它。
结论:vast.template 用 html 编译器操作,方便的一批。后来想想也是,template 默认的 lang 属性就是 html,是我自己瞎折腾,官方也没必要再写一个 template compiler。